Benefits and Costs of Meeting Clean Energy and Carbon Reduction Goals: New Report shows benefits of the energy transition in Wisconsin
In recent years, Wisconsin has set goals to expand clean energy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. At the state level, in 2019, Governor Evers set a goal for 100% carbon-free electricity in Wisconsin by 2050. Utilities across the state have also set carbon emissions reduction targets and have made plans to retire Wisconsin coal plants. These goals signal that Wisconsin is moving toward an energy transformation.
With growing momentum to meet ambitious clean energy and climate goals, RENEW Wisconsin partnered with Clean Wisconsin, GridLab, and Evolved Energy Research in 2022 to evaluate the economic impacts of Wisconsin meeting electricity and carbon dioxide reduction goals. This study resulted in the report Wisconsin’s Roadmap to Net Zero by 2050 (Evolved Report). The Evolved Report includes modeling energy system changes in two primary scenarios. The first scenario models 100% carbon-free electricity by 2050 (100% Clean Electricity), and the second scenario models net-zero carbon dioxide emissions economy-wide by 2050 in Wisconsin (Net Zero Economy-Wide).
The Evolved Report summarizes the benefits and costs associated with these scenarios. However, these summaries do not provide detailed ‘apples-to-apples’ analysis for economic comparisons. For example, the Evolved Report included annual infrastructure investment ‘system’ costs and benefits results over the 2022-2050 time period. Additionally, the Evolved Report provides health benefits using a separate modeling tool that captures benefits in snapshots in time at 2030 and 2050. However, from the perspective of climate change impacts, the Evolved Report does not monetize the benefits of carbon dioxide emissions reductions. To thoroughly compare the cost-effectiveness of these scenarios, RENEW set out to perform a supplementary analysis to bring together and compare the cost and benefits streams between now and 2050 in different modeled scenarios.
To combine the streams of benefits and costs, RENEW conducted a benefit-cost analysis of the cumulative benefits and costs of these scenarios titled Benefit and Cost Impacts of Reaching Clean Energy and Carbon Emissions Reduction Goals in Wisconsin (Benefit Cost Report). Benefit-Cost Analysis (also referred to as cost-benefit analysis) is a process that identifies, monetizes, and compares the effects of alternatives. This form of analysis is often used to compare different policies, programs, or projects. In a real-world example, The Public Service Commission often relies on intensive benefit-cost analysis to weigh a proposed utility project (such as a large solar or transmission facility) against other feasible alternatives. In short, RENEW’s Benefit Cost Report is intended for policymakers, government officials, business leaders, and those skeptical of the clean energy transition or concerned that the negative economic impacts of this transition will outweigh the benefits.
To complete this benefit-cost analysis, RENEW staff worked closely with the lead modeler to receive and understand all the data behind the many facts and figures in the Evolved Report. The RENEW team then analyzed the data by interpolating the time series data and discounting the data over time to accurately compare costs and benefits occuring at the different points over multiple decades. This process ensured value streams were accurately identified, separated, compared on common terms, and not double counted in total results. An additional description of the analytical process can be read in the Approach section of the Benefit Cost Report.
Reaching 100% Clean Electricity Yields High Benefits Compared to Costs, Achieves ¼ of Needed Emissions Reductions
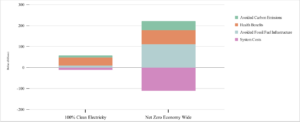
Accomplishing 100% Clean Electricity by 2050 is a cost-effective target, as the benefits far outweigh the costs when all benefits are considered. Meeting 100% Clean Electricity by 2050 would cost an estimated $12 billion between 2023 and 2050 to build new renewable energy infrastructure. But the operation of these renewable energy facilities would avoid fossil infrastructure investments and ongoing fuel costs. The avoided costs of fossil fuels and associated infrastructure, which is an economic benefit of $8.75 billion, is somewhat less than the renewable energy investment alone. However, when considering additional benefits, this is clearly a cost-effective scenario.
The benefits of replacing fossil fuels with clean electricity go beyond the avoided infrastructure and fuel costs. When health benefits and avoided carbon dioxide emissions are also included, the benefits of clean electricity outweigh the costs five to one. For every dollar of investment spent to transition to 100% Clean Electricity, Wisconsin will see $5 in benefits. However, as the Evolved Report details, the 100% Clean Electricity scenario only achieves about ¼ of all carbon emission reductions compared to economy-wide decarbonization.
Economy-Wide Decarbonization in Wisconsin Results in Billions of Dollars of Benefits and Remains Cost-Effective
According to the modeling results, going beyond 100% Clean Electricity to decarbonize the entire economy would cost more money in direct investments but would yield hundreds of billions of net benefits. The estimated economic cost of the Net Zero Economy-Wide scenario is $111 billion from 2023 – 2050. The direct economic benefits from avoided fossil fuel costs will be $111 billion over that same period. The health and climate benefits are much higher in the Net Zero Economy-Wide scenario compared to the 100% Clean Electricity scenario. Including all health and environmental benefits, the benefits outweigh the costs in the Net Zero Economy-Wide scenario by $111 billion. Although net-zero transition requires more investment, the benefits are also higher for Wisconsinites. The more considerable investment associated with the Net Zero Economy-Wide scenario results in a more significant return on that investment for Wisconsin’s economy, as presented in the table below.
Transitioning to a Clean Economy Creates a Healthier Wisconsin
In both scenarios, Wisconsinites would see considerable health benefits by reducing fossil fuel use. These health benefits are measured through an air pollution model that estimates the changes in air pollutants called criteria air pollutants¹.
Reducing our use of fossil fuels will have significant health benefits in Wisconsin, resulting in fewer heart attacks, respiratory and cardiovascular hospital admissions, acute bronchitis and respiratory symptoms, and asthma emergencies. For our analysis, we monetized the low and high-range emissions reductions estimated by the COBRA model and included the monetized benefits in the final benefits calculation of the Benefit Cost Report. In the 100% Clean Electricity scenario, the modeled health benefits are estimated to be between $18 billion and $40 billion cumulatively through 2050. In the Net Zero Economy-Wide scenario, where fossil fuels are reduced further, the health impacts are estimated to be between $30 billion and $68 billion.
Jobs, Jobs, Jobs!
A related report by Cambridge Econometrics, titled The Economic Impacts of Decarbonization in Wisconsin (Cambridge Report), provided estimates of the job growth and Gross State Product (GSP) impacts of decarbonization. The table below summarizes these impacts.
| Scenario | Gross State Product Increase by 2050 | Net Job Growth by 2050 |
| Net Zero Economy-Wide | 3.0% | 68,500 additional jobs |
| 100% Clean Electricity | 0.5% | 7,320 additional jobs |
The results of the Cambridge Report further emphasize the differences in the volume of benefits between the 100% Clean Electricity scenario and the Net Zero Economy-Wide scenario. The Cambridge Report results are clear: full decarbonization will lead to massive job growth and economic development for Wisconsin.
Public-private partnerships and planning will help ensure Wisconsin benefits from the clean energy transition and attracts job creators to our state. An article from Wisconsin Public Radio (WPR) describes the potential of the clean energy economy transition and the challenges ahead. The WPR article highlights a recent Wisconsin Economic Development Corporation report on Wisconsin’s potential for EV component production, and highlights the need to develop workforce training to ensure Wisconsin remains competitive and an attractive location for clean economy manufacturers.
Meeting Clean Energy and Carbon Reduction Goals: A Win-Win for Wisconsin
The analysis performed by RENEW Wisconsin shows that meeting either the 100% Clean Electricity goal by 2050 or the Net Zero Economy-Wide target by 2050 will result in more benefits than costs for the state. Meeting either goal by 2050 is cost-effective, as each dollar invested in energy system changes results in more than one dollar in total benefits. While the 100% Clean Electricity goal is more cost-effective from an incremental perspective, reaching the Net Zero Economy-Wide goal results in greater benefits and achieves economy-wide net zero carbon emissions. Decarbonizing the entire economy requires more investment but results in considerable advantages in terms of avoided fossil fuel costs, health benefits, and avoided carbon dioxide emissions.
Fully decarbonizing Wisconsin’s economy is also critical to meet climate change goals. While transitioning the electric grid to 100% clean electricity is important, focusing only on the electricity sector will not be enough to address the greenhouse gas emissions that cause climate change. The United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has found that keeping global temperatures from rising beyond 1.5 degrees above pre-industrial levels requires net zero carbon dioxide emissions by 2050². This goal is aligned with the 2015 Paris Agreement to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5 degrees C above pre-industrial levels³. The Net Zero Economy-Wide target for Wisconsin is most aligned with this goal and is an important target to prevent the worst impacts of climate change.
Reaching either clean energy goals or broader emission reductions result in benefits, including extensive benefits to human health. RENEW Wisconsin is excited to support the development of clean energy in the state, supporting economic development, human health benefits, and the mitigation of climate change.
Footnotes
1. Analysts used a tool, COBRA (Co-Benefits Risk Assessment Health Impacts Screening and Mapping Tool), to model air pollution changes and the impact on human health. The tool was developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
2. https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/sites/2/2022/06/SPM_version_report_LR.pdf
3. https://unfccc.int/most-requested/key-aspects-of-the-paris-agreement