
by Ben Behlke | Aug 9, 2024 | Home, Inflation Reduction Act, Local Government
With the launch of the Home Efficiency (HOMES) rebate program, Wisconsin is the first state in the country to begin utilizing IRA funds to help homeowners increase the energy efficiency of their homes. Focus on Energy launched the program in August 2024. This groundbreaking initiative is designed to help homeowners improve their home’s energy efficiency in a more accessible and cost-effective way.
How to Get a HOMES Rebate
The goal of the HOMES rebate is to help people improve the efficiency of their homes. One of the first steps in home electrification and energy efficiency is to evaluate the efficiency of your house to better understand where homes are losing energy, whether through leaky windows, poor insulation, or outdated appliances. Since every person consumes energy differently, getting an energy assessment is a crucial first step to understanding your specific situation and in qualifying for a rebate.
HOMES will offer rebates for whole-home energy projects, such as improving insulation, and heating and cooling equipment. Participants can save anywhere from $1,500 to $10,000 on a project, depending on income, whether they live in a single-family or multi-family home, and how much energy they expect to save.
While renters are not eligible to receive a HOMES rebate, you can encourage your landlord or building owner to participate in the program.
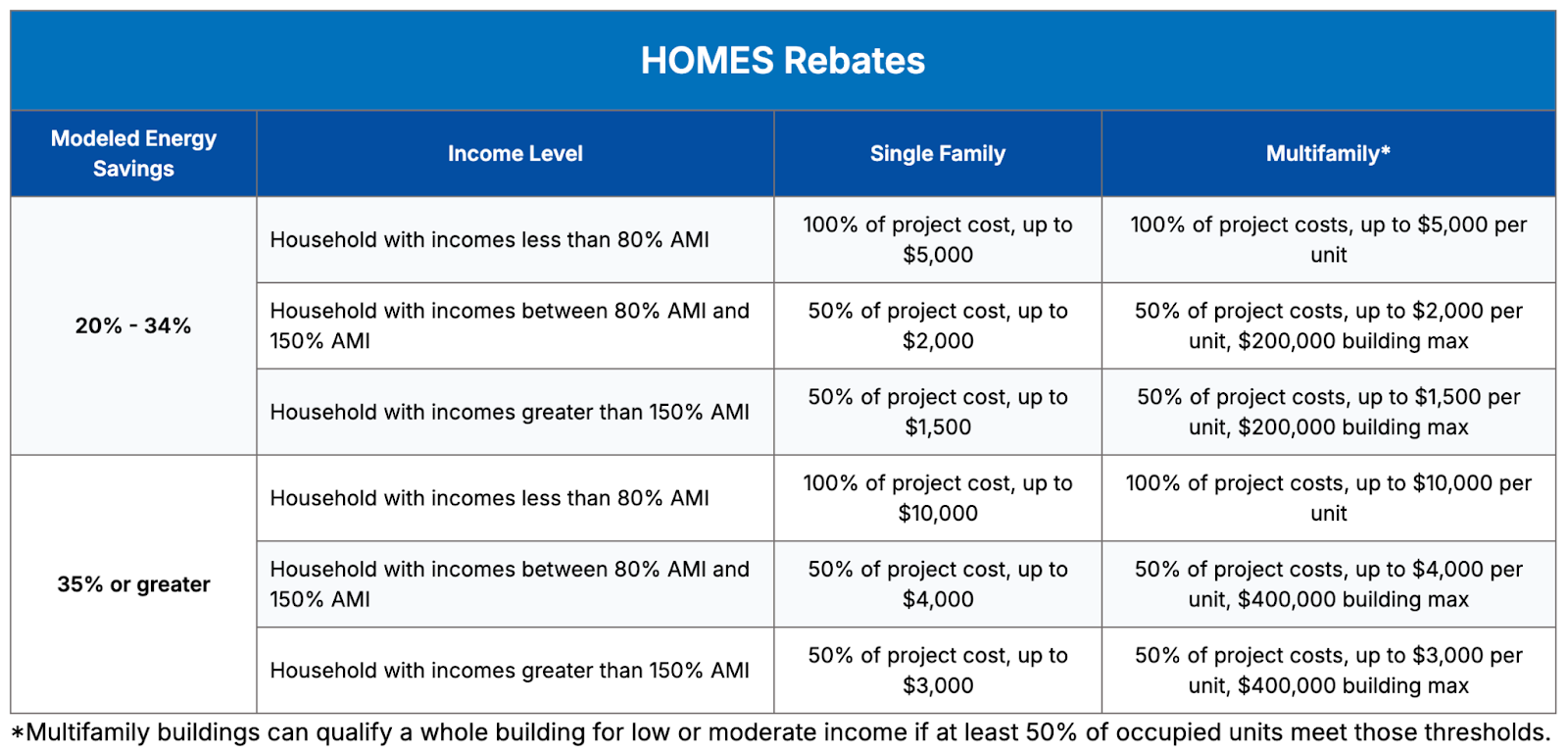
*Table from Focus on Energy
The rebate also has a retroactive aspect. Home Efficiency Rebate projects that started on or after August 16, 2022, are eligible for rebates if they meet specific criteria. To qualify for retroactive HOMES program rebates, projects must comply with all final federal and state program requirements.
Reducing Energy Burden
These rebates offer a crucial first step for many Wisconsinites to become more energy efficient and reduce their energy burden in the process. Energy burden is defined as the percentage of a household’s income that is spent on energy costs, such as electricity, heating, and transportation. According to the American Council for an Energy Efficiency Economy, the average energy burden for Wisconsin is 2 percent, but some low-income households face energy burdens as high as 9 percent. These rebates are a great first step in ensuring more Wisconsinites see their energy burden reduced to a manageable level.
A Cleaner, Healthier Wisconsin
This effort will also help lower emissions from our residential sector. The residential sector is responsible for 8 percent of Wisconsin’s greenhouse gas emissions. In Madison, homes contribute 19.8 percent to the city’s overall emissions. In Milwaukee County, residential energy use made up 25 percent of the county’s total emissions as recently as 2018. By making our air cleaner we not only combat the impacts of climate change, but also collectively benefit associated from fewer days of school and work missed due to illness, less frequent hospital visits, and can lower the localized number of respiratory illnesses.
The rebates also provide a welcome injection into local economies by increasing demand for energy-efficient products and services, which will support new jobs in the energy-efficiency sector. In fact, the U.S. Department of Energy projects that these programs will help families nationwide save around $1 billion each year and create 50,000 jobs within the country.
by RENEW Wisconsin | Jul 31, 2024 | Advocacy, Community, Community Solar, Electrification, Energy Storage, Health, Home, Inflation Reduction Act, Local Initiatives, RENEW Wisconsin, Renewables, Sustainability
The Menominee Indian Tribe of Wisconsin is committed to preserving their environment and fostering sustainable growth. In the face of a rapidly changing climate, investing in clean energy isn’t just about harnessing the power of the sun and wind—it’s about empowering their community, protecting their sacred lands, and ensuring a vibrant future for generations to come. With increased clean energy funding opportunities, such as those provided by the Inflation Reduction Act, the Menominee Indian Tribe of Wisconsin is creating new opportunities, enhancing economic resilience, and supporting the Tribe’s cultural values.
Special thanks to Isaiah Ness (Sun Bear Industries) and Zoar Fulwilder (Mavid Construction Services) for their work to advance clean energy in Tribal communities and for inviting RENEW to witness the transformation.

by Francisco Sayu | May 24, 2022 | Electrification, Home, Sustainability
Co-author: Jenna Greene
Early April 2022, two people were seriously injured in an explosion caused by attempting to light a propane furnace in their Marinette County home. Approximately 253,000 (primarily rural) households in Wisconsin use propane to heat their homes, putting public safety at risk and creating greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that negatively impact human health. In addition, propane is currently the most expensive fuel type for Wisconsin residents. Air-source heat pumps can be a safe, efficient, and affordable alternative to propane heat. Wisconsin needs policies, programs, and incentives that accelerate this transition for rural customers.
An air-source heat pump (ASHP) is an electrically powered heating and cooling device that moves heat, rather than generating it, to provide comfortable building temperatures. ASHPs operate “in reverse” in the summer to provide cooling (similar to a refrigerator). Cold-climate air source heat pumps have made significant technological advances in recent years; today, ASHPs can operate in temperatures as low as -22 degrees Fahrenheit. Some local Wisconsin residents and nonprofit organizations are already switching to ASHPs for heating and cooling.
Heating homes with fossil fuels create emissions that impact human health and contribute to climate change – 8% of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in Wisconsin come from the residential sector. Climate change threatens the economy in many ways, including increased flooding and storm damage, altered crop yields, lost labor productivity, and strained energy systems. Wisconsin’s electric grid is increasingly powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Transitioning away from propane heat will increasingly reduce GHG emissions.
In 2021, Wisconsin imported 41,000 barrels of propane – valued at more than four million dollars. Spending money on imported energy resources weakens local economies and burdens household budgets. Many Wisconsin residents feel the effects of rising fossil fuel costs, with propane projected to be the most expensive fuel source in 2021-2022. Transitioning to air-source heat pumps can lower annual heating and cooling costs and free Wisconsinites from the volatility of imported fossil fuels.
ASHPs provide safe, efficient, and affordable home heating and cooling. Electricity is generated off-site and delivered to homes, which dramatically lowers the safety risk to families from on-site propane combustion. High-efficiency heat pumps can convert one British Thermal Unit (BTU) of electricity into three BTUs of heating or cooling – significantly more efficient than gas furnaces at most temperatures. ASHPs are also cost-effective compared with propane use. ASHP adopters can save up to $750 per year on heating and cooling costs. We need financing mechanisms to allow households and businesses to finance energy efficiency retrofits and ASHP installations with affordable upfront payments.
Many rural Wisconsin households use propane or heating oil to heat their homes which is expensive, puts people at risk, and sends millions of dollars out of state each year. Wisconsin utilities, policymakers, and Focus on Energy should expand programs to transition households from propane heating to efficient electric heating, saving people money, reducing hazards, and improving health outcomes in rural communities.

by Guest Blog | Nov 24, 2021 | Community, Focus on Energy, Home, Renewables, Solar, Sustainability
Beneficial electrification discussions often revolve around transportation electrification, specifically how electrifying vehicles can reduce emissions and offer cost savings for consumers. However, an under-discussed and equally important part of beneficial electrification is the building sector. At 24% direct emissions, the building sector comprises the largest end-use emissions in Wisconsin. Read further to learn about Susan Millar’s journey towards electrifying her home, including her installation of an air-source heat pump for greater heating and cooling energy efficiency.
The companies, technologies, and programs endorsed in this blog are not necessarily recommended or endorsed by RENEW Wisconsin. The following information and personal experience is illustrative of the process to electrify a residential property in Wisconsin.
Are you wondering how to convert an older single-family home with a forced hot-air heating system, a gas water heater, and a gas stovetop from gas and electric to electric-only? I have done that with a 90-year old house on the near west side of Madison. And because it took a fair amount of time, I am sharing the process I used. Before describing this process, I provide important context.
Context for Transitioning to All-Electric
- “Natural” gas is fossil gas. It must, and will, be phased out over time as our society gets more serious about reducing climate-warming emissions. In some municipalities, bans on gas in new construction are already in place.
- Air source heat pumps (ASHPs) are the energy-efficient electric-powered alternative to gas heating systems. ASHPs both heat and cool your house (no separate AC device needed). They have a high coefficient of performance, so while they use electricity, the amount is much less than, say, what an electric space heater or traditional AC unit uses. See, for example, this video description of ASHPs.
- Air source water heaters (also called “hybrid” water heaters) work the same way as ASHPs except they exchange air with your basement instead of the air outside. They are far more efficient than traditional electric water heaters.
- Our state’s Focus on Energy program provides rebates for air-source air and water handling systems. The installers handle this process. (I am not sure of the size of these rebates.)
- MG&E’s monthly (gas) service charge is $22. If you stop your gas service and start it again, they will bill you for monthly service charges for up to 12 months prior to the time you start again. That is, you cannot stop your gas service except for, say, the month of January without paying for up to 12 months of service.
- If you have not yet, or cannot install, solar panels on your roof, you can sign up for MGE’s shared solar program.
- If you have an EV and are willing to charge it and also run your dishwasher, etc during MG&E’s low-rate (off-peak) period (from 9 pm to 10 am on weekdays, and during weekends and holidays), you can substantially reduce your electricity bill. To do this, call MG&E and ask them to add you to their ‘Time Of Use’ program.
- Yes, you have to lay out money ahead of time to transition from gas, and I am aware that many people cannot do this. The financial payoff comes over time. For example, while paying both gas and electric service charges, and charging my EV at home, my MG&E bill this summer was between $20 -30 per month. This is largely due to having rooftop solar and Time Of Use electricity rates. While my utility bills will be higher this winter, they will be reduced by the $22 monthly gas service charge and will be substantially less than prior winters. For me, another major advantage is that I am emitting essentially no carbon dioxide to run my home and car.
Steps for Transitioning to All-Electric (used by an early adopter)
- Get an energy efficiency analysis. This is very important because if you switch from a furnace powered by an unlimited amount of gas to an ASHP, it’s important that your house holds its temperature (in winter or summer) as effectively as possible. I used a local energy efficiency consultant. He did a superb job.
- Improve your insulation. If your energy efficiency analysis indicates that your house needs insulation, then arrange to get it. I used a small local company that treated my home as if it was their own. I felt the difference immediately, even in summer.
- Replace your gas stovetop (both to get off of gas and because much new research indicates respiratory health problems are caused by gas stovetops). As I have a unit with an electric oven and gas stove, I purchased two Cuisinart’s Double Induction Cooktops (not expensive), which I placed over the gas burner area on my stove and just plugged in. (Induction stovetops work great, and are much easier to keep clean.)
- While doing steps 1 & 2, get contracts with the HVAC and plumbing company you will use. I started with the local HVAC company that I was used to. They proposed an ASHP system that would heat my house to +14F degrees and required that I retain my gas furnace for backup in the winter. As I want to eliminate the year-round monthly gas service charge, I turned them down. I tried 3 other local companies. Same response. I looked wider and found a company located near Milwaukee. In light of the energy efficiency and size of my house, they proposed to replace my gas furnace and AC units with a Mitsubishi P system that will efficiently heat my house to -14F, and then shift to an electric element (low efficiency) backup system for super cold snaps. Their price? Same as the local HVAC folks who proposed installing a +14F system with gas back-up. I accepted Midwest’s proposal. Moreover, they agreed to install my (still effective and efficient) gas and AC units in the home of a friend who has very inefficient HVAC systems – so the embedded carbon in those devices is not immediately trashed. (FYI, I informed the local HVAC companies of my decision – they lost my business to a more cutting-edge, non-local competitor.)
- Meanwhile, after checking different local plumbers, most of whom do not install hybrid water heaters, I found a small local plumbing company that proposed to install one of these at a very decent price. I happily accepted his bid.
- Both the HVAC and plumbing companies I signed with encountered installation delays because ASAP and hybrid water heater manufacturers are having sourcing issues. These problems are either due to Covid shipping issues or because the manufacturers are sending their stock to states that are ahead of us on installing these systems. Demand pushes the market.
- Both the hybrid water heater and the ASHP have easy controls and work superbly. For the mid-October to mid-November billing period, the first during which I used electricity to heat water, heat the house, and charge my EV, I used 664 kWh. My MG&E bill was $54. In round numbers, they charged me $42 for connection and distribution services, $15 for contributions to their Shared Solar, Green Power, and Low-Income Assistance programs, and $37 for electricity used at variable rates. (I have “Time of Use.” Most of my use was at the very lowest rate.) They credited me $39 for “net energy exported at variable rates” (kWhs from my solar panels), and $2 for “fuel cost.” All that suggests that I paid $-2 for electricity provided by MG&E.
- If you would like cost or contact information for the energy efficiency, insulation, HVAC, plumbing, and electrician contractors I used, just email me at sbmillar@gmail.com.
Susan Millar, September 2021

by RENEW Wisconsin | Oct 26, 2021 | Advocacy, Community, Community Solar, Electric Vehicles, Events, Home, Jobs, Legislative Watchlist, Local Government, Policy, RENEW Wisconsin, Renewables, Solar, Sustainability
On October 13, RENEW Wisconsin and Wisconsin Conservative Energy Forum (WCEF) hosted their first-ever Renewable Energy Day at the Capitol in Madison. The event included issue briefings by industry experts on a variety of legislation that has been introduced this year related to the solar and electric vehicle industries. Attendees then went to the State Capitol to speak with their legislators to gain support for these important issues.
During a welcome reception, the evening before the Day at the Capitol, RENEW and WCEF held a panel discussion “Energy in Transition: Policy and Politics.”
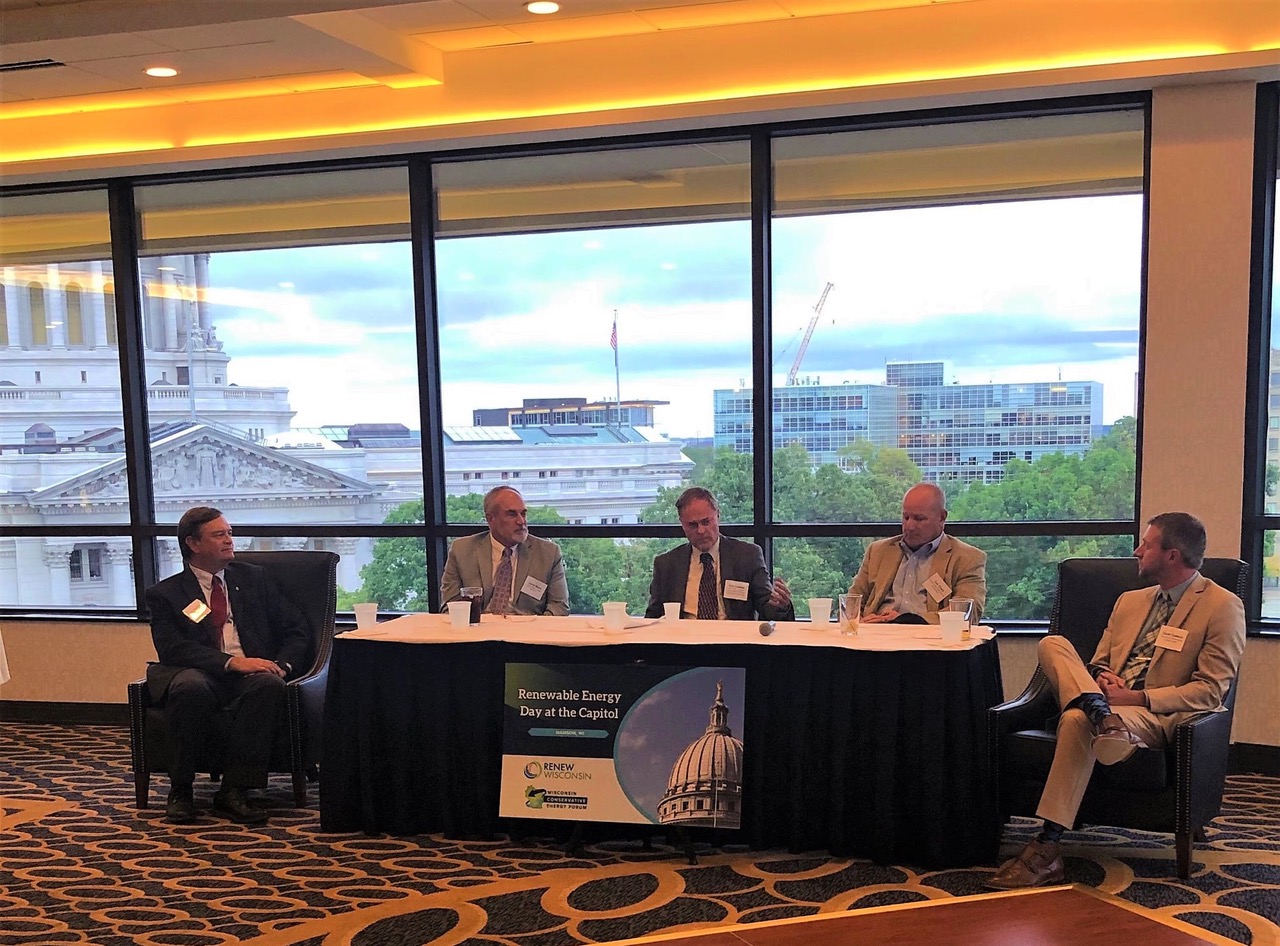

From right to left were moderator, Scott Coenen (WCEF), Dan Ebert (former PSC Chairman), Senator Rob Cowles, Larry Ward (Conservative Energy Network), and Jim Boullion (RENEW Wisconsin).
The panel discussed the current uncertainty in world energy markets and the impact that energy shortages and spiking prices will have on the world. There was consensus from the conversation that panelists believe renewables can help stabilize much of this energy uncertainty, but that the industry needs to be realistic about its role in a world where supply is not meeting demand. Businesses, households, and communities in Wisconsin should be empowered to invest in their own energy generation.
Before attendees went to the Capitol to meet with their legislators, there was an issue briefing with a panel of industry experts moderated by Jim Boullion, Director of Government Affairs for RENEW Wisconsin. The panelists explained in detail what legislative proposals were currently before the legislature, how they will impact renewable energy in Wisconsin, and what arguments are being made on both sides of the issue.
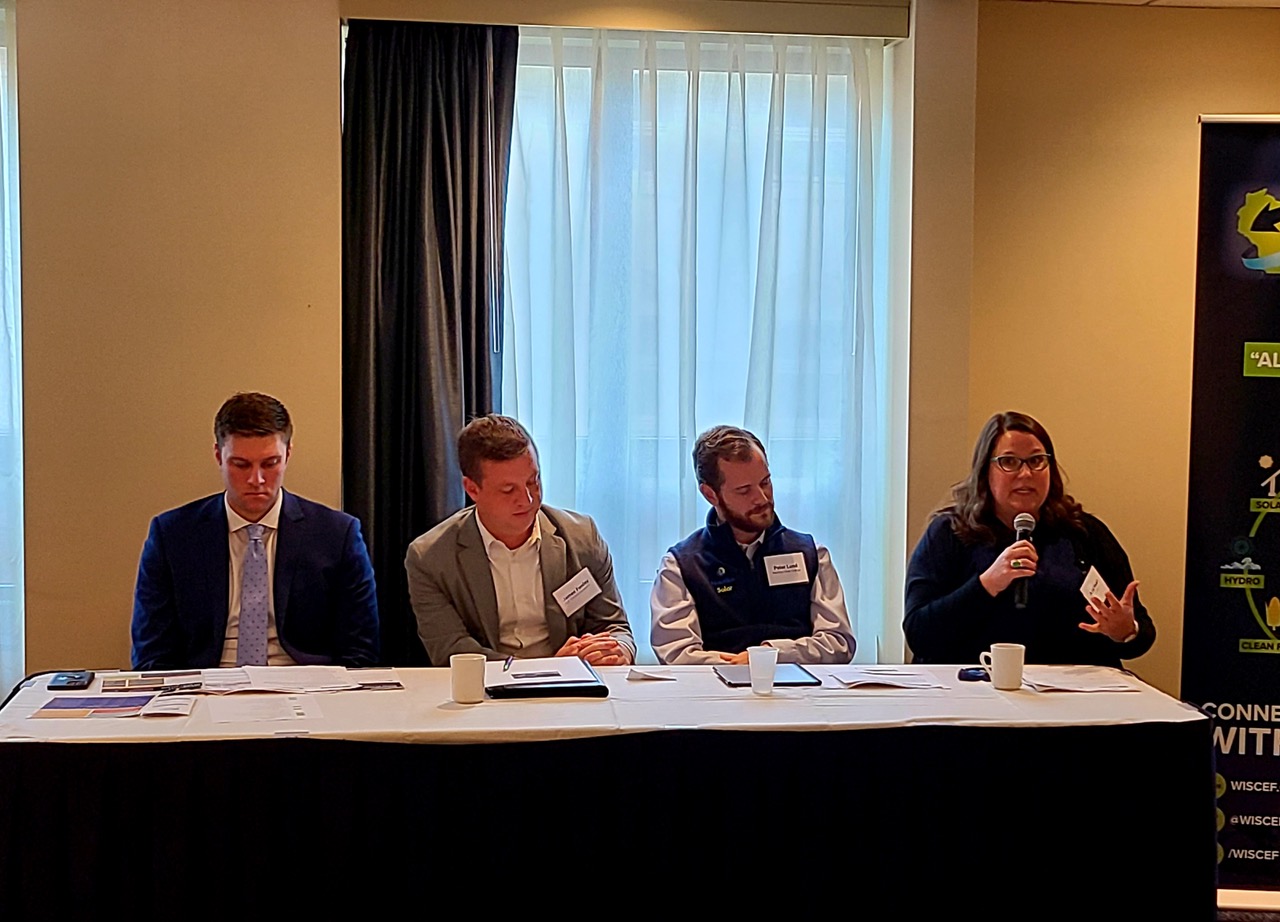

Issue briefing panelists, Left to right: Jason Mugnaini (Chief of Staff, State Senator Rob Cowles), James Fenley (SJL Government Affairs & Communications), Peter Lund (Financial Structuring Associate, Nautilus Solar Energy), and Amy Heart (Senior Director, Public Policy, Sunrun).
The first panel discussed two solar-related issues:
- Expanded Development of Community Solar – (SB 490 / AB 527 – Sen. Stroebel and Rep. Ramthun) This bill would authorize the development of non-utility owned community solar projects and provide access to the economic and environmental benefits of solar for those who can’t afford the full cost of a system, live in multi-family housing, or own property that is not suitable for solar.
- 3rd Party Financing/Leasing – (LRB 1550/1 Sen. Cowles and Rep. Cabral-Guevara) This legislation would clarify that 3rd party financing/leasing of renewable energy equipment is legal in Wisconsin, providing affordable financing options for people, businesses, municipalities, or not-for-profit entities who don’t have the resources to pay for solar on their own property.
The second panel, moderated by RENEW’s Jeremy Orr, Emerging Technology Program Manager, discussed electric vehicle issues such as Wisconsin’s recent Direct Electric Vehicle Sales legislation, SB 462 / AB 439 (Sen. Kooyenga and Rep. Neylon). Albert Gore, Policy and Business Development at Tesla, discussed how allowing manufacturers to sell electric vehicles directly to consumers creates greater access to the electric vehicle market, resulting in growth in the traditional dealership model. Read Jeremy Orr’s previous testimony on this issue here.
Likewise, Justin Ackley, Public Policy Manager at ChargePoint, spoke to the business clarity and consumer transparency that AB 588 / SB 573 (Sen. Cowles and Rep. VanderMeer) would provide, as it would allow non-utility-owned charging stations to charge by the kWh. Similar to a gas pump, where the price per gallon is displayed, kWh charging tells electric owners how much energy they’re paying for, regardless of how long it takes to charge their vehicle. The panel pointed out that while the main goal of this legislation is good, another section of it would create problems by prohibiting charging a fee if any of the electricity going through the EV charger comes from a non-utility source such as a solar+storage system.
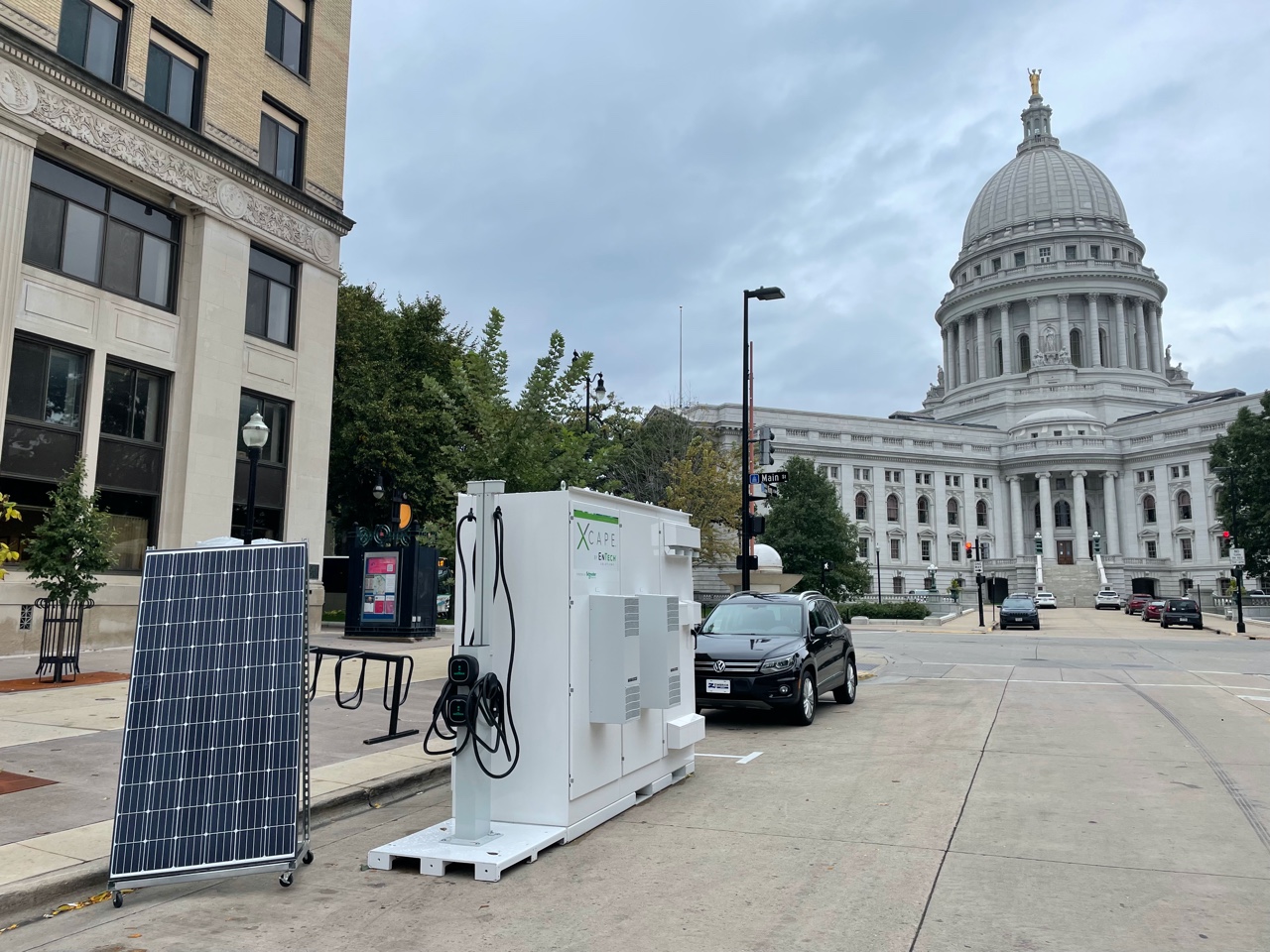
Emerging technology allows EV chargers to be installed in areas, especially rural areas, that have inadequate grid infrastructure and can help limit costly spikes in energy “demand charges” for charging station owners. EnTech, a division of Faith Technologies based in Menasha, Wisconsin brought one of their portable solar+storage units to Capitol Square to demonstrate how the technology works and how flexible it can be. A similar system was set up at Bergstrom Ford in Neenah to help reduce the energy bills at their dealership. John Bergstrom, the owner of the dealership, told the story of why he worked with Faith Technologies to install the system in this podcast.

The panel closed the session by discussing two other bills recently introduced by Sen. Rob Cowles:
- $10 million in VW Settlement Funds for EV Charging Station Grants – (LRB-0254/1 Sen. Cowles and Rep. VanderMeer) Grants from these funds would be used to install electric vehicle charging stations at key locations throughout Wisconsin.
- Energy Storage Sales Tax Exemption – (LRB-1513/1) – Sen. Cowles and Rep. Duchow) This legislation would clarify that battery storage devices installed as part of a renewable energy system should be included in the sales tax exemption that already exists for renewable energy system equipment.
The 75 registered attendees made an impact by taking time out of their busy lives and getting involved in the political process. None of these issues will be easy to pass. In fact, most of them face significant opposition from powerful forces. But working together and building coalitions with pro-renewable energy friends helps get important legislation like this adopted.
If you would like to learn what you can do to help as well, contact Jim Boullion, Director of Government Relations at jim@renewwisconsin.org.








