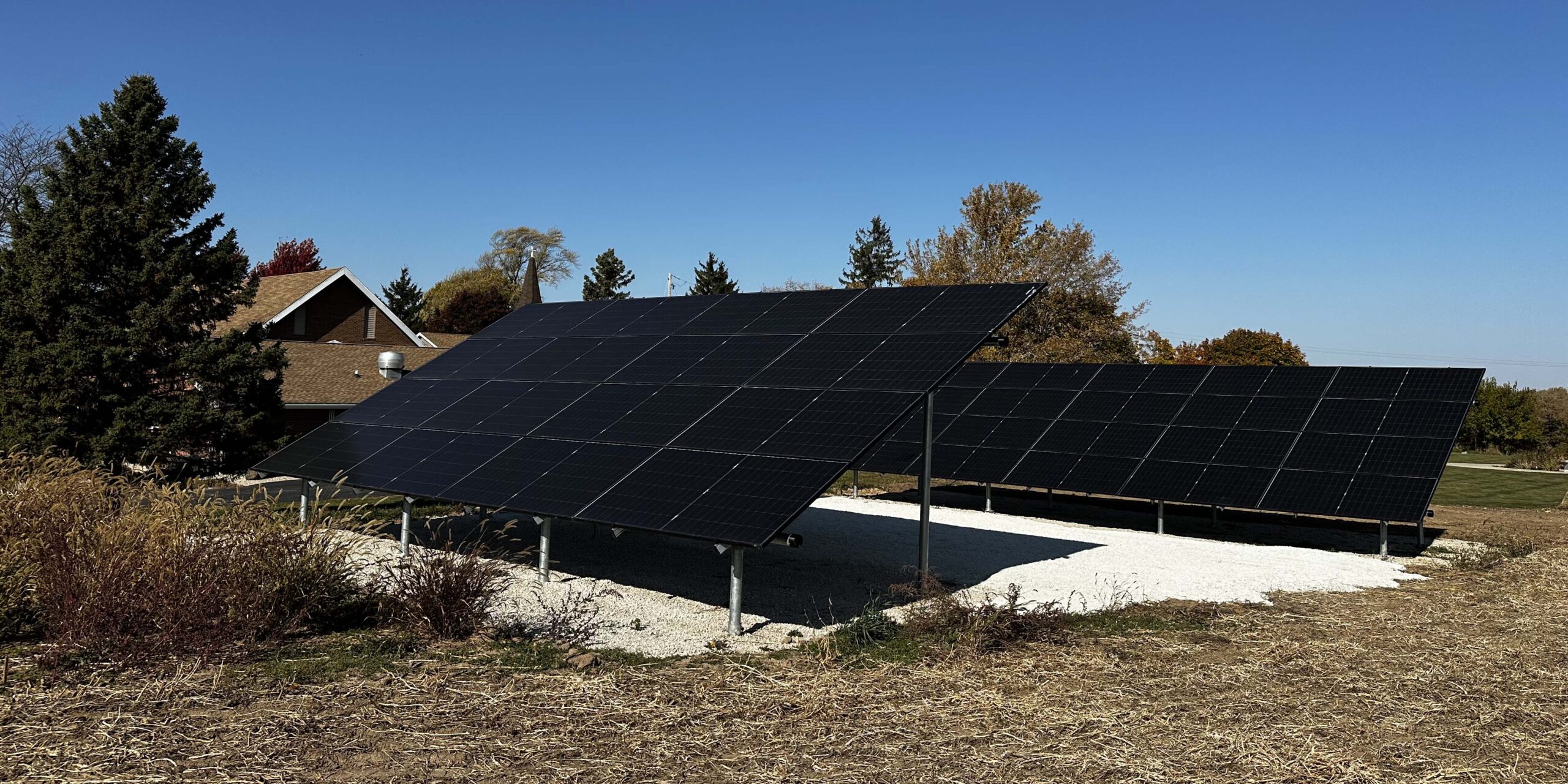
Sugar Creek Lutheran Church Solar Project: Powering the Future of Community Programs
Sugar Creek Lutheran Church, a beacon of faith and community, has long been committed to improving the lives of its congregation and the surrounding Elkhorn area. For over 175 years Sugar Creek has uplifted nearby residents through outreach initiatives for underserved families and youth engagement programs. The church’s commitment to sustainability has also been at the heart of its mission, leading it to embark on a transformative renewable energy project: a solar power system that will provide long-term financial stability while enhancing its community outreach efforts.
By investing in clean, renewable energy, Sugar Creek Lutheran Church not only took steps to reduce its environmental impact but also set in motion a series of financial and community benefits that will continue to reverberate for years to come.
A Mission-Inspired Project
Solar Project Lead Ervin Schlepp understands the church’s mission of sacrificial love for others to include acts of service for both his community and the natural world. With a background in engineering and wastewater management, this long-time Elkhorn resident found the perfect opportunity to marry his faith and professional experience in leading his congregation’s transition to renewable energy.
“Part of our decision to proceed with this project was not only to be better stewards of the environment and to reduce our carbon footprint but also to allow us to make use of the money we save from utility bills, which we know will be higher in the future,” Schlepp said.
Educating and Engaging the Community
Seeing solar installation as a golden opportunity to increase financial savings, community service, and environmental stewardship, Schlepp was eager to garner his congregation’s support. To foster collective understanding and excitement for the solar project, throughout 2023 the Church published monthly newsletters and held educational seminars on both how solar power works and what benefits its adoption would bring to the congregation.
These engagement efforts allowed project leaders to address concerns and gather valuable input that would shape the project’s final design and implementation. Collaboration with the congregation, community members, and local partners resulted in a final plan that closely aligned with their collective needs and vision. When it came time to hold a vote on the solar project, 94% of the congregation was in support!
Funding the Future
Key to the success of the project was a thoughtful and strategic approach to funding. Schlepp and other project leaders understood the importance of securing financing before beginning construction, ensuring they would not be burdened by financial strain during development. Through a combination of grant funding, state programs, and the Inflation Reduction Act’s direct pay program, Sugar Creek received a total of $54,142 in funding for its solar project.
Some of the key funding sources included:
- Solar for Good: The Couillard Solar Foundation and RENEW Wisconsin’s collaborative program donated 18 panels valued at $6,500
- Solar Moonshot Program: Hammond Climate Solutions Foundation’s program awarded $25,000 in grant funding
- Focus on Energy: This Wisconsin program contributed $2,947 towards Sugar Creek’s project
- Congregational Support: Donations from its congregation covered the remaining upfront project costs and prevented the need for a bridge loan
- Direct Pay: Sugar Creek expects to receive $19,695 in clean energy tax credits and a bonus credit of $6,565 for using American-made steel and iron
By balancing various funding streams, Sugar Creek ensured that its solar project was not just a financial success, but also an example of how to maximize available incentives and minimize risk.
Designing a Vision for Change
After securing project funding, Sugar Creek employed local experts Adams Electric Solar Group and We Energies’ solar engineering staff to ensure the solar system’s design would meet energy needs while staying under budget. The church also integrated solar-powered electric heat pumps into their heating system, further reducing reliance on propane and lowering overall energy costs.
“The overall project process and completion took us approximately 14 months,” Schlepp said. “Much of that was our learning about solar panel power systems and our process to get congregational approval plus raising our portion of the funding required.”
These investments in time, technology, and education bolster the church’s commitment to sustainability as it transitions away from non-renewable energy sources and secures long-term savings that can be redirected to essential community programs.
Unexpected Challenges and Community-Based Solutions
By leveraging community expertise and resources, Sugar Creek streamlined its solar installation and demonstrated the power of grassroots problem-solving in making renewable energy more accessible. Church leaders encountered an unexpected hurdle of needing a conditional use permit. While the property was zoned for solar, installations of its size required additional approval. Fortunately, the church’s strong relationships with town and county officials helped expedite the process and they secured approval in just two months—far faster than usual. The Walworth County Board’s experience with the church led them to eliminate the conditional use permit requirement for similar solar projects, making it easier for other organizations to pursue renewable energy.
Another challenge arose when the metering panel needed replacement to meet current standards, and an additional snow and ice protection overhang was needed for the panel’s safety. A local contractor stepped in to install the upgraded metering panel, while a church member who owned a fabrication manufacturing facility volunteered to design and build the protective overhang. This collaborative effort kept the project moving forward while also strengthening local businesses and deepening connections within the congregation.

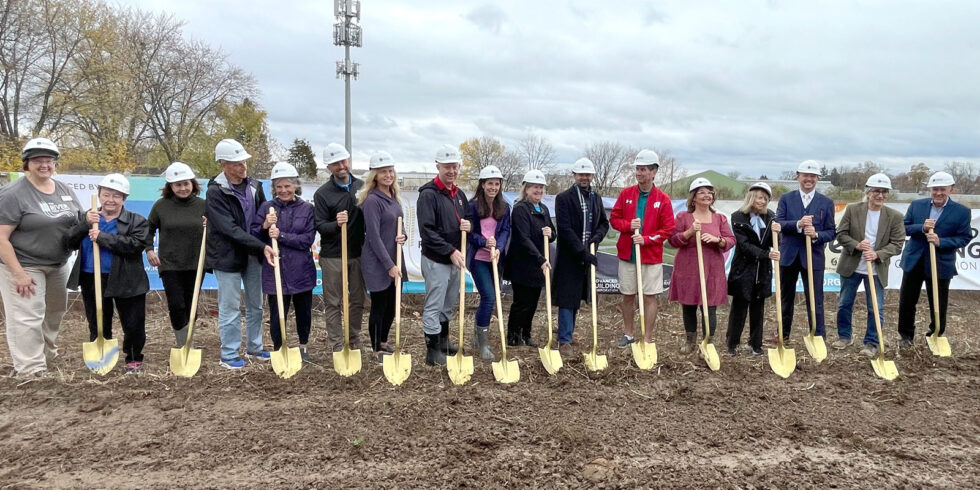
Solar Project Lead Ervin Schlepp, Pastor Dick Inglett, and Walworth County Board District 3 Supervisor Brian Holt break ground at the project site in July 2024.
Looking Ahead
Since Sugar Creek’s solar array was placed into service, the church has welcomed the significant reduction in utility bills.
“It is exciting to see that as an organization we were willing to capitalize on solar power and that we did not say ‘our old system is good enough’ and move on, but decided that an integrated system for our facilities allows us to generate more electricity than we need,” Schlepp said.
The success of this solar project is just the beginning. The church is exploring additional sustainability initiatives, including expanding its solar array and installing updated, efficient heating units to further reduce reliance on fossil fuels. The church is also continuing its educational outreach to inspire other local organizations to pursue renewable energy.
“Reducing our carbon footprint and teaching others about the benefits of solar power is important to our congregation,” Schlepp said.
As the congregation continues to see the positive impact of its solar project, they are more determined than ever to reinvest savings into the programs that make a tangible difference in the lives of the people they serve. The church plans to expand its support of vital community programs like the local food pantry, continuing education scholarships, and adult day care for individuals experiencing dementia — a win for both the environment and the community.
Sugar Creek Lutheran Church’s solar project demonstrates that with careful planning, strong community involvement, and a commitment to sustainability, nonprofits can achieve both environmental and financial benefits. The church’s solar project proves that nonprofits can lead the charge on the path to a more sustainable and equitable Wisconsin. By reducing their carbon footprint and enhancing their financial sustainability, the church has created a model for other organizations to follow.
Each day since installation, Schlepp said they enjoy tracking the system’s energy generation on a mobile app. “It warms my heart to know that on a sunny day, we are creating more power than we are using, and the system is working well.”
For more information on how to fund a similar project, reach out to info@renewwisconsin.org.