
by Michael Vickerman | Mar 16, 2021 | Policy, PSC Priorities, Public Service Commission, RENEW Wisconsin, Renewables, Solar, Utilities
After simmering on the proverbial back burner for nearly two years, the third-party financing issue relating to customer-sited solar power has been thrust back into the public spotlight as pressure builds to resolve the legal questions surrounding it.
The reemergence of this issue can be traced to two parallel developments. The first is a Public Service Commission (PSC) proceeding moving toward a ruling settling the legality of third-party-owned solar systems serving individual retail customers. The second is a lawsuit recently filed by the Midwest Renewable Energy Association in Portage County Circuit Court, challenging the PSC’s authority to regulate the financing of behind-the-meter systems that serve host customers only.
The PSC proceeding began in March 2019 when Eagle Point Solar, a Dubuque-based solar contractor, filed a complaint against We Energies for blocking the installation of rooftop arrays serving the City of Milwaukee. In its complaint, Eagle Point contends that PSC Chapter 119, which regulates the interaction between small-scale electricity producers and the utility grid, does not give We Energies the right to deny interconnection to a customer based on how the generating equipment is financed. According to We Energies, however, a third party owner of the equipment that supplies electricity to one customer under contract should be regulated as a public utility.
Following an extended period of legal maneuvering, the PSC set in motion a process for investigating Eagle Point’s complaint (Docket 9300-DR-104). In so doing, it expanded the scope of the proceeding to consider the public utility question that led to the interconnection denial. When the parties finished entering evidence into the hearing record, the PSC opened a public comment window on the proceeding, which ended on February 23rd.
Supporters of third-party financing sprang into action, led by RENEW. To illustrate the breadth and depth of support for opening up the solar market in this fashion, RENEW circulated an action alert encouraging those who care about this issue to submit comments supporting Eagle Point’s position. Networks such as Wisconsin Climate Table, Wisconsin Health Practitioners for Climate Action, and our own solar contractor e-mail list helped circulate RENEW’s alert beyond our own activist base. At the same time, organizations such as 350 Madison and Environmental Law and Policy Center (ELPC) asked their activists and members to post comments on the PSC website.
As a result of our combined efforts, a total of 336 individuals and organizations weighed with their views on the Eagle Point matter. Of that, 327 comments expressed support for opening the market to allow third-party ownership of solar electric systems in Wisconsin. In that overwhelming display of support, several themes prevailed, including the following:
- Third-party financing is already expressly authorized in 28 states;
- Allowing third-party-owned solar systems is consistent with Wisconsin case law;
- The threat of being regulated as a public utility discourages businesses from providing solar power generated onsite to retail customers through leases and sale agreements;
- Third-party financing would make solar power affordable to low-to-moderate income households and nonprofit entities such as schools;
- Expanding solar financing options would help communities reduce their reliance on harmful fossil energy sources; and
- Expanding solar financing options would invigorate local economies.
These arguments track closely to those articulated by Wisconsin solar contractors and consultants in a March 2019 filing urging the Commission to approve Eagle Point’s petition. Similar to our efforts during the comment period, RENEW shaped the themes in that statement and pulled together a coalition of market actors to demonstrate support for third-party financed solar energy. In the intervening two years, Eagle Point Solar and the City of Milwaukee labored to amass a set of facts and legal arguments to support a finding that WEPCO’s action was unlawful.
The merits of this case are clear-cut, as are the regulatory remedies. Other states that regulate electric utilities have taken steps to affirm the legality of third-party-financed solar, most notably Iowa, which did so in 2014, the result of a long and expensive legal fight waged by Eagle Point. In contrast to Iowa, the State of Wisconsin has allowed this issue to languish for many years without resolution.
But with the filing of briefs from parties on March 10th, the Eagle Point proceeding has finally reached the home stretch. The strong outpouring of public support for third-party financed solar tells us that a policy call from the PSC is long overdue.
In a brief representing RENEW and other solar advocates, we urged the PSC to take the following actions:
- Order WEPCO to interconnect the City of Milwaukee solar projects, regardless of how those projects are financed;
- Clarify that a utility may not deny interconnection based on project ownership, and
- Clarify that third-party owners of customer-sited distributed generation are not “public utilities” under Wisconsin law.
RENEW would like to thank Eagle Point Solar and the City of Milwaukee for leading this crucially important regulatory battle, ELPC for drafting a particularly persuasive legal brief on behalf of clean energy advocates, and the 327 commenters who affirmed their desire for an expanded solar marketplace free of utility interference.

by Heather Allen | Mar 8, 2021 | Health, Local Government, Public Service Commission, Renewables, Solar, Utility Scale
Onion River Solar is a proposed 150-megawatt solar generating facility to be located in southern Sheboygan County that will feature a prairie and pollinator environment. Ranger Power is developing the project and others in the state, including Badger State Solar and Crawfish River Solar, in Jefferson County, and Western Mustang Solar in northwest Wisconsin.
Photos from the North Star Solar project in North Branch, Minnesota, illustrate the type of pollinator and prairie habitat that will accompany Onion River. While grazing is not yet part of the Onion River project, the North Star Solar photos demonstrate the potential to graze livestock between solar panel rows, an exciting opportunity for solar in Wisconsin.
The Onion River Solar project will produce clean, cost-effective electric energy for Alliant Energy customers, provide a diversified income source for local farmers, and generate significant tax revenues for the town and county. This project can improve environmental outcomes ranging from reduced air emissions, reduced chemical use on local farmland, increased grassland and pollinator habitat and improved downstream water quality in parts of the Onion River watershed.
Onion River Solar is anticipated to avoid the generation of over 400 million pounds of CO2 per year. For more information on solar farms’ potential to reduce air emissions, you can see RENEW’s analysis of the 250 MW Darien Solar Farm’s health benefits.
The solar farm is expected to generate $250,000 per year in new revenue to the Town of Holland and $350,000 per year to Sheboygan County. Local governments can use these funds to meet pressing local budget priorities.
Onion River Solar represents a significant step forward to build Wisconsin’s renewable energy capacity and to shift away from fossil fuels.
The Public Service Commission is accepting comments on this project which must be received no later than Tuesday, March 16, 2021.
Additional project information, including a map, are available at www.OnionRiverSolar.com. If you have questions, please contact the project at (888) 898-8878 or info-wisconsin@rangerpower.com.

by Sam Dunaiski | Feb 25, 2021 | Renewables, Solar, Utilities, Wind
The unfolding situation in Texas remains dire. The grid operator, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) first warned of rolling blackouts on Sunday, February 14, 2021. The blackouts and widespread power outages lasted for days in the Lone Star state amidst some of the harshest winter weather in years. Millions of people were left without power and dozens perished.
Now just ten days out from the onset of the crisis, water contamination and shortages (resulting from frozen and broken pipes) continue to threaten the health and welfare of Texas residents.
Immediately preceding the energy crisis, a powerful winter storm blanketed the southern Plains with freezing rain and snow, followed by record low temperatures. Frigid temperatures had a stranglehold on the central U.S. for two straight weeks, extending from Canada to Mexico. Many parts of Texas and the South rely on electricity as their primary source of heat, as opposed to gas, propane, or wood, which are more commonly used in the northern United States. The prolonged cold snap created a high demand for natural gas, for both heating and electricity generation around the region, triggering an upsurge in electricity consumption.
Everything that could go wrong, did go wrong
As demand skyrocketed, supply plummeted. Even before the winter weather moved in ERCOT had nearly 14 gigawatts (GW) of electric-generating capacity offline for maintenance. As other generating sources were shuttered, ERCOT was left with as much as 34 GWs of electric production offline. This periodically amounted to 30-42% of ERCOT’s total electric capacity.
Unfortunately, the outages gave rise to a disinformation campaign that attempted to implicate frozen wind turbines as the principal cause of the power outages. This narrative is patently false. While some wind turbines were frozen and unable to produce electricity, the cold and ice had a far more disruptive effect on thermal plants.
Operators at ERCOT and researchers identified the critical failure of natural gas to generate electricity and heat during the crisis. Nearly 50% of ERCOT’s natural gas generators were offline, either a result of frozen lines or diminished supplies as demand for the fuel soared.
Wind, natural gas, and other energy sources need to be weatherized
In fact, renewable energy generation facilities played a key role in keeping the lights on. According to ERCOT, wind power output exceeded forecasted generation numbers during the blackouts, even with the icing of turbines. At times, solar generation has also exceeded output. Wind turbines would have done better if they had used heating technology as Sweden does, to prevent icing and keep turbines generating power in extreme cold. Using heating carbon-fiber technology similar to aircraft, Swedish maintenance workers add a thin layer of material to the wings of the turbines that can be automatically heated can prevent ice before it forms.
The bottom line is that our electricity grid and all types of power generation are vulnerable to extreme weather events. We need to plan for these events and invest in grid resilience and weatherization to prevent disasters like this from repeating.
There is no single cause for the situation currently unfolding in Texas, and no silver bullet for preventing a repeat situation. A combination of record demand due to the prolonged cold temperatures, and generators not equipped to function in very cold temperatures are responsible for the rolling blackouts now plaguing the state.
Planning and preparing for extreme weather has to be part of the conversation
Renewables are reliable sources of energy from Texas to Antarctica. Even during extreme weather events, wind and solar can function when traditional energy sources have gone offline. More renewable energy sources, in more locations, will diversify our grid and make it less susceptible to the forces of nature and the market. Microgrids and energy storage are important tools to help shore up the reliability and safety of our grid.
Extreme weather events will continue to complicate our lives and strain our power grids over the foreseeable future. By incorporating more sources of renewable energy, we can reduce problems and increase reliability in our electric grid.

by Jim Boullion | Feb 24, 2021 | Legislative Watchlist, Policy, Renewables
On Tuesday, February 16th Governor Tony Evers presented his 2021-23 Budget Bill proposal, SB 111. Among the 1,848 pages of the $91 billion budget RENEW Wisconsin has identified 28 proposals that are directly related to clean energy and energy efficiency. A short summary of the individual issues can be downloaded HERE.
The bill now goes to the Joint Finance Committee (JFC) for review. The JFC will hold a series of public hearings, likely in April, to gather public comments and then will spend the next several months amending the bill. Once the bill passes out of Joint Finance, it goes to both houses of the legislature for final review and potential amendment there. The Session Calendar indicates that the legislature plans to finish the budget and adjourn for the summer by June 30th.
RENEW Wisconsin will be closely monitoring the progress of the bill and working to pass as many of the Governor’s clean energy and efficiency proposals as possible. If you would like to talk to your legislators about any of these provisions, or if you have ideas that you think the State should adopt into the Budget Bill, you can click here for a directory to find contact info for your state representative.
If you have any questions or comments feel free to contact Jim Boullion, RENEW Wisconsin’s Director of Government Affairs at jim@renewwisconsin.org.

by Lauren Reeg | Feb 17, 2021 | Energy Storage, Renewables, Solar, Utility Scale
3.11.2021 Update: After the initial posting of this blog, further research indicates that the Darien Solar Energy Center would have a *capacity factor likely closer to 0.24, not .30. Using this updated capacity factor of .24 for the Darien Solar Energy Center, emissions would decrease by 423,000 tons of carbon dioxide (CO2), 602,000 pounds of nitrogen oxides (NOx), 745,000 pounds of sulfur dioxide (SO2), and 76,000 pounds of particulate matter (PM10) annually for the lifetime of the project. These emissions reductions would lead to decreased mortality of about one life per year, annual health savings between $15 to $34 million, and yearly climate savings of over $17 million
* Capacity factor expresses in percentage form the expected production of a power plant relative to its maximum possible output. This ratio takes into account variables such as maintenance-related downtime and the availability of the energy source fueling the plant. All power plants have a capacity factor of less than one.
Consider a solar farm sized to produce a theoretical maximum of 10,000 megawatt-hours/year. If the plant is estimated to have a capacity factor of 0.30, it can be expected to produce 3,000 megawatt-hours a year. A solar farm could not have a 1.0 capacity factor because the sun doesn’t shine all day. In fact, with nighttime constituting half of the hours in a year, a solar farm could not have a capacity factor greater than 0.50.
The Darien Solar Energy Center is a proposed 250-MW solar PV facility in Walworth county, Wisconsin currently under review at the Wisconsin Public Service Commission. If approved, developers hope to have the project constructed and energized by 2023, offering significant health, environmental, and economic benefits to local Wisconsin communities.
Using the EPA’s Avoided Emission and Generation tool, RENEW Wisconsin estimates that the Darien Solar Energy Center could reduce emissions by 538 thousand tons of carbon dioxide (CO2), 700 thousand pounds of nitrogen oxides (NOx), 1 million pounds of sulfur dioxide (SO2), and 98 thousand pounds of particulate matter (PM10) annually for the lifetime of the project. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change, and sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter contribute to health problems including asthma, cardiopulmonary disease, and premature mortality. Fossil fuel power plants are the primary emission sources of these pollutants. Transitioning to the clean energy produced by the Darien solar project, Wisconsin would reduce its fossil fuel generation, providing significant human health and environmental benefits to its residents.
RENEW Wisconsin completed in-house research on the health benefits of the Darien project. Using the EPA’s Co-Benefit Risk Assessment model, the Darien Solar Energy Center is estimated to reduce mortality by up to one life per year for 30 years in Wisconsin. The health impacts are substantial for Wisconsin, a state highly dependent on coal-fired electricity generation. Energizing the Darien Solar Energy Center could directly save Wisconsin lives.
In addition to the health benefits of clean energy, there are also significant economic benefits this solar project could deliver. Using the EPA’s health benefit factors for Wisconsin, the annual savings ranged from $18 to $42 million depending on population, pollution burden, and other differentiating factors. Moreover, Darien could produce up to $22 million in annual savings resulting from avoided climate impacts. Climate impacts are estimated from the EPA’s social cost of carbon values. These monetized health impacts are significant and illustrate the benefits that the Darien Solar Energy Center could bring to the Wisconsin economy.
Overall, these findings detail the benefits that the Darien Solar Energy Center offers Wisconsin by reducing pollution, decreasing human mortality, helping to mitigate climate damages, and providing millions of dollars in economic benefits to the state. Other significant benefits related to Wisconsin GDP, employment, and environmental and water impacts were not discussed in this article. To learn more about the Darien Solar Energy Center and its additional benefits, please visit the Town of Darien website.

by Heather Allen | Jan 28, 2021 | Advocacy, Community, Policy, PSC Priorities, Public Service Commission, RENEW Wisconsin, Renewables, Solar
COAUTHORS: Michael Vickerman and Lauren Reeg
Wisconsin’s distributed generation (DG) renewable energy market lags behind comparable states.[1] As seen in other states, DG helps diverse groups of individuals and organizations, including businesses, residents, renewable energy customers, and future renewable energy customers, gain access to renewable energy and create a more fair and navigable market.
Whether it takes the form of behind-the-meter generators powering individual customers or larger projects feeding power directly into the distribution grid, DG is a vitally important segment of the renewable energy landscape. Customer investments drive these installations with benefits extending to Wisconsin businesses, residences, governments, nonprofits, and their communities. DG clean energy investments help spur local economic investment, support clean energy jobs, and save Wisconsin money that otherwise would have been spent on importing fossil fuels.
It has long been RENEW’s view that a more fair, clear, and consistent regulatory environment could strengthen the DG market and accelerate the transition to renewable energy in Wisconsin.
In June 2020 the Public Service Commission of Wisconsin (PSC) convened an investigative docket” (5-EI-157) to identify regulatory barriers that effectively put a tight lid on Wisconsin’s DG market, especially customer-sited DG.
This investigation is structured to encourage input and recommendations from organizations and entities that support small-scale DG. RENEW has assembled an expert legal and technical team for this docket—Tim Lindl and Melissa Birchard of Keyes and Fox, and Justin Barnes of EQ Research. We invite you to review the legal and policy analysis we provided to the PSC in August 2020 and in January 2021.[2] A coalition of organizations (Clean Energy Advocates) joined our comments to the PSC, demonstrating broad support for an improved DG market. This ongoing investigation is the best opportunity we’ve had in more than 10 years to advance renewably powered DG before the PSC.
The success of this campaign will strengthen and expand the renewable DG market in Wisconsin. If you support this work, please consider a donation to RENEW today. Together we can champion renewable energy growth in Wisconsin and we are poised to make significant progress in 2021. Join us today!
Wisconsin has fewer net metering customers than comparable states
Net metering customers represent an important segment of the renewable energy market, however, Wisconsin is falling behind. In the last four years, net metered customers in Wisconsin have grown by only 0.11%, well below the increases seen elsewhere in other states since 2015.
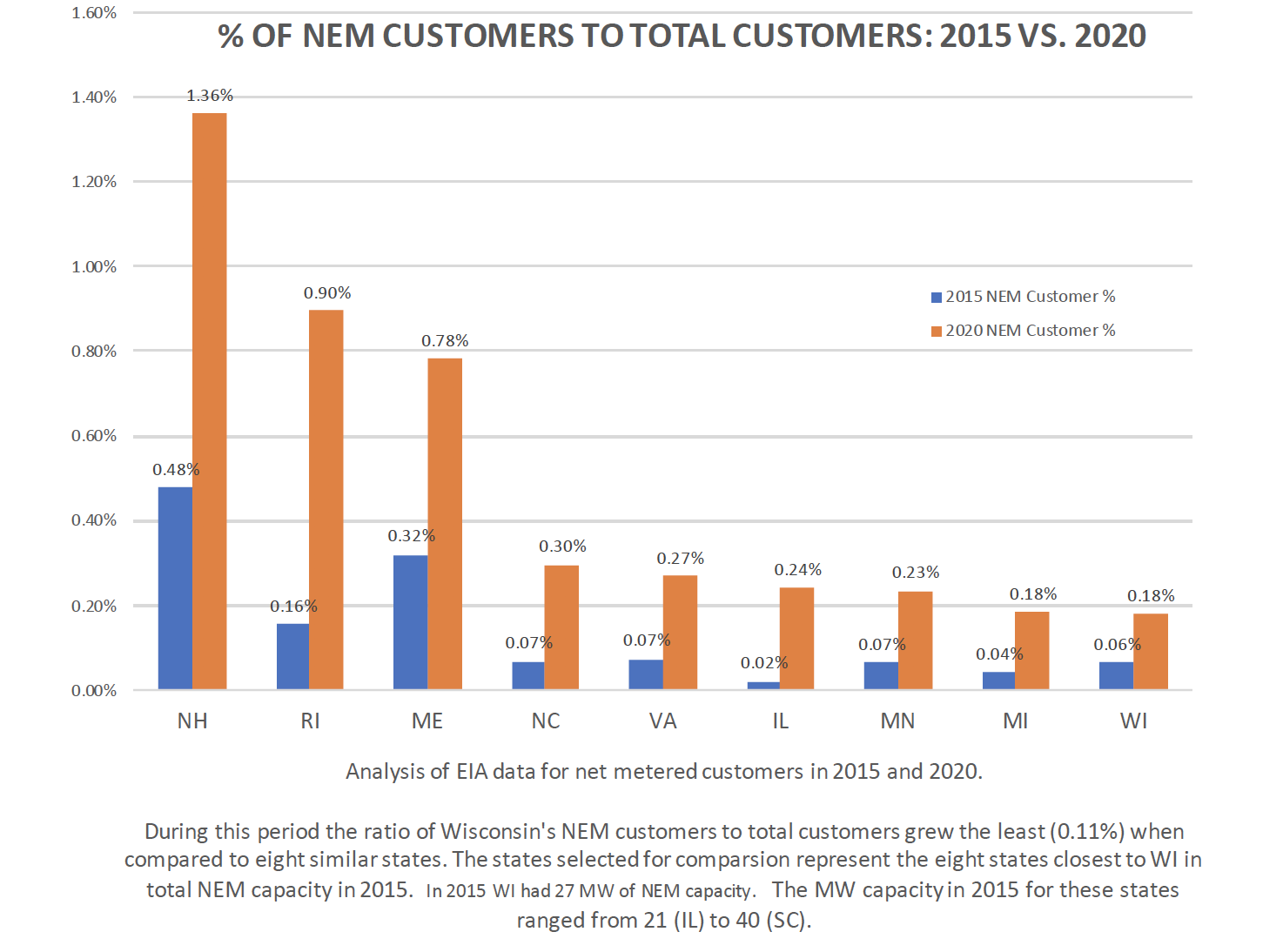
Fair and clear distributed generation policies would grow the renewable energy market in Wisconsin
RENEW Wisconsin aims to enlarge the market share for non-utility-owned renewable DG, including both self-supply and grid-supply projects. In furtherance of that goal, we’ve developed a number of principles that should inform decisions rendered in the DG docket. These include:
- Ensuring developer access to standard offer contracts that have terms for reasonable compensation.
- Giving developers insight into system and utility resource needs to help them target their planned investments.
- Provide larger energy users with better and less restrictive opportunities for larger self-supply resources.
- Standardize and improve net metering rates for all customers across Investor-owned Utilities (IOUs).
In addition to behind-the-meter systems, RENEW has also set forth a path for front-of-meter renewable generation projects up to 20MW. These types of projects should be eligible for 20-year standard offer contracts that are pegged to the same methodologies that utilities use when assigning value to their own generation projects. Leveling the playing field for compensating solar is essential to increasing customer investment opportunities, and expanding the solar workforce.
RENEW is optimistic that by the end of the docket the PSC will land on several beneficial policy changes for promoting renewable DG. These policy changes could be taken up later this year through the anticipated utility rate case filings. Should events unfold along these lines, solar developers and customers stand ready to benefit from a more fair, clear, and consistent renewable energy market.
Join RENEW’s campaign to advance renewable distributed generation in Wisconsin
Since 1991, RENEW has been the state’s preeminent advocate for renewable energy. At the macro scale, solar and wind can outcompete fossil fuels on cost and environmental performance. For the first time in more than a decade, we have an opportunity in Wisconsin to broaden the clean energy transition underway to benefit all customers who place a value in a healthy energy economy. A clear, fair and forward-looking regulatory environment will be crucial to spreading renewable energy across all sectors of society. RENEW is bringing together the leadership and expertise necessary to undo the regulatory barriers that have held renewable DG back, and to replace them with policies to make renewable DG more accessible, affordable, and plentiful across Wisconsin. We hope you will join us in this work by donating today. 2021 promises to be an exciting year!
[1] RENEW evaluated eight states closest to Wisconsin in terms of cumulative Net Energy Metering (NEM) capacity at the end of 2015, i.e., the four states immediately above and below Wisconsin in EIA data listing NEM capacity by state. The eight states closest to WI in NEM capacity in 2015 included NH, RI, ME, NC, VA, IL, MN, and MI. The 2020 data is based on NEM capacity through April 2020. The percentage of total customers uses 2018 total state customer counts for both calculations. Note that Wisconsin has fallen behind states it had previously led. See bar graph for more information.
[2] In the most recent comments filed by Clean Energy Advocates, we looked at this year’s PSC calendar to assess how our recommended actions can make their way into regulatory policy. The DG docket now underway is well-timed in that we expect every Class A investor-owned utility in Wisconsin to file for new rates in 2021.







