by jboullion | Apr 13, 2010 | Uncategorized
From an article by Tom Content in the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel:
A revised state clean energy and global warming bill unveiled Tuesday scales back the scope of the bill but retains a commitment to expand use of renewable energy and open the door to construction of nuclear reactors in Wisconsin.
The revisions, obtained by the Journal Sentinel, were drafted in response to concerns raised by business groups and politicians that the original bill was too unwieldy, too controversial and potentially too costly.
Jettisoned from the package were mandates concerning transportation fuels, including a requirement that Wisconsin require greater use of low-carbon transportation fuels such as biofuels.
To reduce the overall cost of the package, the bill allows energy efficiency gains to count toward a portion of a mandate that 25% of Wisconsin’s electricity come from renewable power sources by 2025.
A combined energy efficiency and renewable energy standard is also part of federal legislation that passed in the U.S. House of Representatives last year.
The state bill would allow one-fifth of the mandate to come through energy savings, most likely from major energy saving initiatives by factories and other big energy users.
Another change responds to concerns raised by utilities concerning a mandate that had been in the earlier bill concerning small renewable energy projects around the state. The mandate has been replaced with expanded funding for small renewable energy projects. The new proposal states a preference that much of that money be allocated toward manure digesters on Wisconsin dairy farms.
The latest version also underscores the consequences of the weak economy and declining sentiment for taking action on global warming.
Doyle signed an executive order creating the task force in April 2007 – well before the collapse in the economy. In December 2009, after details were known, many business groups attacked it and said the recommendations would harm the energy-intensive manufacturing sector.
But some other industries and companies, notably Johnson Controls, the state’s largest public company, said the bill would create jobs and align the state to take advantage of emerging trends in sustainability.
At the same time, the public appears less concerned about climate change. A national Gallup Poll in March showed that the percentage of respondents who believe the seriousness of global warming is “generally exaggerated” has increased from 35% to 48% in two years.
“As introduced, the Clean Energy Jobs Act would reduce greenhouse gas emissions, create jobs, and help keep rising energy bills in check,” said Keith Reopelle, senior policy director at the environmental group Clean Wisconsin, said in a statement. “The substitute amendment represents a compromise that will still accomplish all of these goals, but to a lesser degree than the original bill.”
Clean Wisconsin is still reviewing the details of the changes.
“As we understand them, the changes in the substitute amendment will result in even more jobs and lower energy bills in the next few years by increasing short-term commitments to energy efficiency,” Reopelle said. “However, paring back the renewable energy standard will likely result in less rate relief in the long term, because renewable energy helps hedge against the rising cost of fossil fuels.”
by jboullion | Apr 13, 2010 | Uncategorized
From an article by Tom Content in the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel:
A revised state clean energy and global warming bill unveiled Tuesday scales back the scope of the bill but retains a commitment to expand use of renewable energy and open the door to construction of nuclear reactors in Wisconsin.
The revisions, obtained by the Journal Sentinel, were drafted in response to concerns raised by business groups and politicians that the original bill was too unwieldy, too controversial and potentially too costly.
Jettisoned from the package were mandates concerning transportation fuels, including a requirement that Wisconsin require greater use of low-carbon transportation fuels such as biofuels.
To reduce the overall cost of the package, the bill allows energy efficiency gains to count toward a portion of a mandate that 25% of Wisconsin’s electricity come from renewable power sources by 2025.
A combined energy efficiency and renewable energy standard is also part of federal legislation that passed in the U.S. House of Representatives last year.
The state bill would allow one-fifth of the mandate to come through energy savings, most likely from major energy saving initiatives by factories and other big energy users.
Another change responds to concerns raised by utilities concerning a mandate that had been in the earlier bill concerning small renewable energy projects around the state. The mandate has been replaced with expanded funding for small renewable energy projects. The new proposal states a preference that much of that money be allocated toward manure digesters on Wisconsin dairy farms.
The latest version also underscores the consequences of the weak economy and declining sentiment for taking action on global warming.
Doyle signed an executive order creating the task force in April 2007 – well before the collapse in the economy. In December 2009, after details were known, many business groups attacked it and said the recommendations would harm the energy-intensive manufacturing sector.
But some other industries and companies, notably Johnson Controls, the state’s largest public company, said the bill would create jobs and align the state to take advantage of emerging trends in sustainability.
At the same time, the public appears less concerned about climate change. A national Gallup Poll in March showed that the percentage of respondents who believe the seriousness of global warming is “generally exaggerated” has increased from 35% to 48% in two years.
“As introduced, the Clean Energy Jobs Act would reduce greenhouse gas emissions, create jobs, and help keep rising energy bills in check,” said Keith Reopelle, senior policy director at the environmental group Clean Wisconsin, said in a statement. “The substitute amendment represents a compromise that will still accomplish all of these goals, but to a lesser degree than the original bill.”
Clean Wisconsin is still reviewing the details of the changes.
“As we understand them, the changes in the substitute amendment will result in even more jobs and lower energy bills in the next few years by increasing short-term commitments to energy efficiency,” Reopelle said. “However, paring back the renewable energy standard will likely result in less rate relief in the long term, because renewable energy helps hedge against the rising cost of fossil fuels.”
by jboullion | Apr 6, 2010 | Uncategorized
A news release issued by Advocates for Renewable Energy, a coalition which includes RENEW Wisconsin:
For Immediate Release
April 6, 2010
For More Information Contact:
Shaina Kilcoyne: (608) 310-3338
As the article below chronicles, Wave Wind LLC, a Dane County-based wind services company, is ready to build a six-turbine, 10-megawatt project in western Dane County and sell the electricity to the local utility, Madison Gas & Electric (MGE). All the necessary permits have been issued and the turbines are set to be delivered in June.
Unfortunately, Wave Wind cannot find a buyer for the project’s output. MGE contends that it does not need new supplies of renewable electricity until after 2020. Moreover, wholesale power prices are at historic lows, and the standard buyback rate available to third-party power producers like Wave Wind is not sufficient to make the project economically viable. As Wave Wind president Tim Laughlin put it, the standard rate “won’t even allow us to put a shovel in the ground.”
The upshot? Wave Wind will likely install those turbines in another state. Should that happen, most, if not all, of the jobs and business opportunities created by the construction and operation of this facility will follow the turbines to the state in which they are installed. Wisconsin’s loss will be a gain for Iowa or New Mexico.
This is not an isolated phenomenon, nor is it limited to wind energy. Dairy operations and food processors looking to recover energy from their organic wastes also find it difficult to justify investments in biodigesters, even with Focus on Energy incentives. A policy solution is clearly needed to bridge the difference between the production costs of small-scale renewable energy systems and the cost of operating 40-year-old coal plants that have been fully amortized. Neighboring Minnesota now has nearly 500 megawatts of community wind due to a statute that encourages it. Such projects have a very minor impact on overall electric rates. Within the Clean Energy Jobs Act, Wisconsin has the opportunity to promote small-scale renewable energy projects as well.
Two provisions in the Clean Energy Jobs Act are tailored to help producers of locally available renewable energy overcome the economic barriers cited above:
+ A 10% in-state renewable energy set-aside by 2025. This provision would more than double the output from existing renewable generating units in Wisconsin.
+ Incentives and other provisions targeted for smaller renewable generating facilities. These provisions would encourage small-scale, community-based renewable projects throughout the state.
Developing a truly sustainable platform to support Wisconsin’s economic future requires a commitment to local energy sources like wind, organic wastes, wood, solar, and small-scale hydro. Passing the Clean Energy Jobs Act will make it easier to attract and retain the private sector enterprises that drive job growth as well as strengthen rural economies.
by jboullion | Apr 6, 2010 | Uncategorized
From a report by Chuck Quirmbach on Wisconsin Public Radio:
(STATE CAPITOL) A key lawmaker says some compromises have been reached in the global warming bill now in the State Legislature. But he says more deal-making is ahead.
During the last couple of weeks, legislators have been working behind closed doors trying to agree on changes to the Clean Energy Jobs Act. At an energy forum in Milwaukee, Senate author Mark Miller said some agreements have been reached. The Madison-area Democrat says there are deals on idling of trucks, reducing carbon in transportation fuels, tariffs for utilities purchasing power from renewable sources, and whether to link Wisconsin car fuel efficiency standards to California’s. He says the golden state plan is gone.
Miller says the plan to reduce carbon in fuels ran into a lot of opposition, and wasn’t a major part of the bill. The changes are good news to the Democrats leading candidate for governor, Milwaukee Mayor Tom Barrett. Barrett says any new carbon in fuels standard would also have hurt the state.
Sen. Miller says lawmakers are also trying to accelerate job creation goals in the Clean Energy Jobs Act. He says he’s hoping to announce final compromises next week.
by jboullion | Apr 5, 2010 | Uncategorized

A news release issued by Advocates for Renewable Energy:
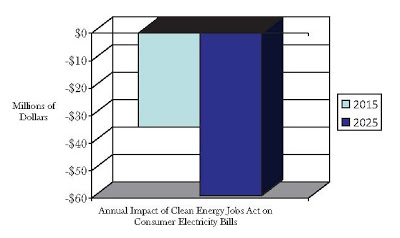
The Union of Concerned Scientists has released a study on the 25% Renewable Portfolio Standard and Energy Efficiency provisions within the Clean Energy Jobs Act (CEJA), confirming the findings of the Public Service Commission that CEJA will result in lower electricity bills than under a business as usual approach.
With a 25% Renewable Portfolio Standard, consumer electricity bills will be $34 million lower in 2015 and $59 million lower in 2025, compared with a business as usual approach. CEJA will result in cumulative cost savings to electricity ratepayers of $140 million by 2025. The report concludes that the Clean Energy Jobs Act will protect consumers from rising energy prices by investing in local sources of energy with stable and predictable long-term costs.

